Al-Arab Blog - مدونة العرب

٢٠٠٤/٠٣/١٩
News Coctail Testifying on American Failures

In a statement sent today to the Arabic language daily al-Hayat, the Abu Hafs al-Masri Brigades, which claimed responsibility for the Madrid bombings that killed 201 people, also urged its European units to stop all operations.
"Because of this decision, the leadership has decided to stop all operations within the Spanish territories... until we know the intentions of the new government that has promised to withdraw Spanish troops from Iraq," the statement said.
"And we repeat this to all the brigades present in European lands: stop all operations."


WAVE OF DEADLY ATTACKS CONTINUE IN IRAQ TODAY
Tony Blair yesterday denounced as "hopelessly naive" the suggestion that pulling out of Iraq would remove Britain from the terrorists' sights.
In his first public comments since Jose Luis Rodriguez Zapatero, the Spanish Prime Minister-elect, threatened to bring home the country's 1,300 troops in Iraq, Mr Blair, echoing comments by President George Bush, urged the world to "stand firm" against terrorism or be defeated by it.
But a defiant Mr Zapatero made clear he would not bow to President Bush's demand to stand by the American-led occupation of Iraq.
He said in a radio interview yesterday: "I will listen to Mr Bush, but my position is very clear and very firm. The occupation is a fiasco. There have been almost more deaths after the war than during the war."
How the US set Pakistan Aflame


Ayad Bressem, an Iraqi boy, his younger brother in the picture background, American bomb blinded him in one eye. Now the Occupation forces of the USA plans to give his family $5,000 and 'I'm Sorry'
What does he think of that now? What would he think of that later ?
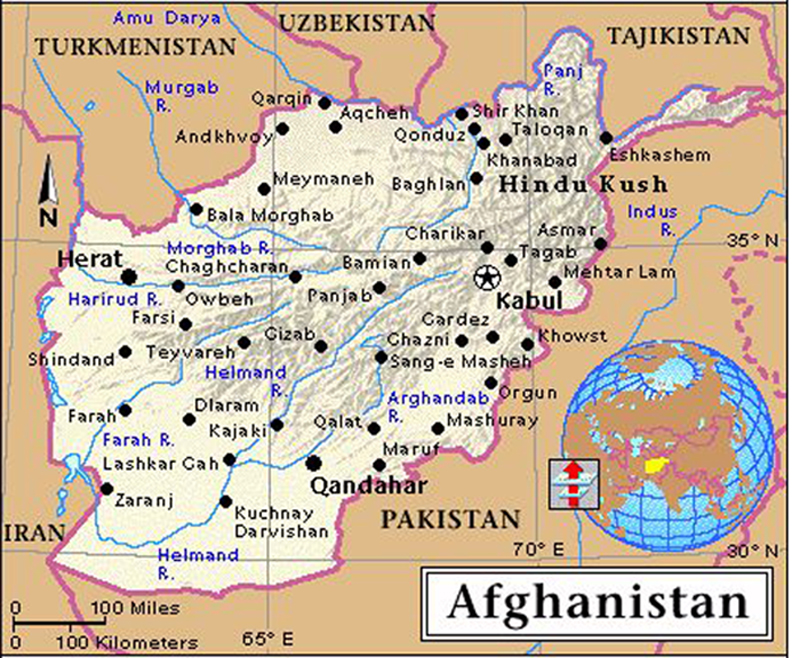
Marauding Taliban and drug-dealing warlords on the road to Kandahar.
by KATHY GANNON, 2004-03-15
Mullah Muhammad Khaksar is a burly man in his early forties with a thick, curly beard that falls halfway down his chest. He lives in a modest house in a poor suburb of Kabul, but he travels often to Kandahar, the largest city in southern Afghanistan, where he was born and where his family owns an electronics shop. When I first met Khaksar, in 1999, he had two grand houses in the center of Kabul, with servants and manicured gardens. The Taliban controlled the city then, and Khaksar was the deputy minister of interior. He was something of an oddity among the Taliban, in that he collected books and would furtively scour the few bookstores that were still open, looking for volumes written in Pashto, the language spoken by most Afghans in the south and the east. He also had a stash of photographs, which were forbidden under the Taliban, and he showed me pictures that had been taken of him when he was fighting the Soviets alongside one-eyed Mullah Omar. Khaksar is a heavy smoker, and even though Mullah Omar had ordered his ministers to give up cigarettes, Khaksar refused to quit. Like his smoking, our meetings were often conducted in secret.
Khaksar was a founding member of the Taliban movement, which arose in Kandahar in the early nineties. After the defeat of the Soviets by the Afghan mujahideen in 1989 and the collapse of the Afghan communist government in 1992, Kabul had been taken over by mujahideen factions that fought bitterly. Meanwhile, Kandahar was at the mercy of violent, thieving warlords. Their militias stopped cars at every other intersection to demand money or weapons. Even Hamid Karzai, Afghanistan’s current president, who is also from Kandahar, supported the Taliban’s intervention in the anarchic post-Soviet period.
In the early years of the movement, Khaksar was the Taliban intelligence chief in Kandahar, but he lost power when he began speaking out against influential Afghan mullahs who had been trained at Pakistani religious schools and were manipulated by Pakistani intelligence officers. The mullahs and, later, Osama bin Laden had ingratiated themselves into Mullah Omar’s inner circle. “I asked Mullah Omar, ‘Why do we need these people?’” Khaksar recalled not long after I met him. “‘The jihad’”—against the Soviets—“‘is over. They should go back to their country.’” Many of the men who had helped found the Taliban could no longer even arrange a meeting with Mullah Omar.
The Taliban sent Khaksar to Kabul in 1996, shortly after they took control of the city, and he was demoted to deputy minister. In April, 1999, he travelled to Peshawar, in Pakistan, where he spoke with J. Peter McIllwain, the C.I.A. chief there. Khaksar told McIllwain that the Taliban could not be defeated militarily by the Afghan opposition, but that the leaders who were most closely aligned with Osama bin Laden and the Pakistanis could be undermined if more moderate elements within the Taliban were supported by arms and money from the West. Khaksar risked a great deal to make this overture to the United States. He knew that Osama’s intelligence was good and that the meeting could cost him his life. Before Khaksar returned to Afghanistan, McIllwain gave him half of a five-rupee note and told him not to talk to anyone who claimed to represent the United States unless he had the other half of the note. The clandestine encounter, as Khaksar described it, sounded like an episode in a cheap spy novel, but McIllwain recently confirmed the details of the meeting, and Khaksar still has his now tattered half of the five-rupee note, along with a letter from McIllwain saying that the Americans were unwilling to do as he asked.
When the Taliban fled Kabul, after dark on November 13, 2001, Khaksar stayed behind. I was in Kabul then, too, and was for nearly three weeks the only Western journalist in the city. The Taliban had encircled Kabul with tanks, and on that last night checkpoints were manned by skittish young men with rocket launchers and automatic rifles. American jets circled overhead, and rockets from gunships slammed into pickup trucks carrying Arab fighters. Smart bombs hit several buildings, including one next to my office, which had been home to the Taliban’s police chief and defense minister.
Khaksar’s decision to remain in Kabul identified him publicly as a traitor. This does not cause problems for him in Kabul now, since nato forces police the streets. But in the south and the east, where the Taliban live and where they have been increasingly active in recent months, killing and kidnapping with impunity, Khaksar has to move more carefully. He drives to Kandahar perhaps once a month, even though many people along the route know who he is.
“It’s my country,” Khaksar said to me in December. “If God decides it’s time, then it is time.” His bravado seemed a little reckless, since on his most recent trip to Kandahar several men with Kalashnikovs had opened fire on his vehicle, a four-wheel-drive S.U.V. with a license plate and ownership papers supplied by the Afghan intelligence service. (Khaksar is vague about what he does in Kandahar, saying only that he meets with tribal leaders and “talks about the future of Afghanistan.”) He described hitting the gas pedal and raising a blinding cloud of dust that caused him to smash into some road-construction equipment. Khaksar smiled as he talked about the attack. He was sitting on the carpeted floor of his house, propped up on red cushions that rested against a whitewashed wall, and his smile revealed that he had lost two teeth in the crash.
You don’t have to be a Taliban defector to feel a little queasy about taking the road from Kabul to Kandahar. In the past year, an Italian tourist travelling on the road in a taxi was shot dead; four Afghans working for a Danish relief agency were killed; two Afghans working for the Afghan Red Crescent and four security guards working for the Louis Berger Group—an American firm that was hired by the United States Agency for International Development, usaid, to work on the road—were ambushed and killed; a Pakistani and a Turkish engineer were killed; two Turkish engineers, two Indian engineers, an Afghan driver, and an Afghan employee of an American aid organization, Shelter for Life, were kidnapped; and dozens of vehicles have been fired upon. Early in February, two men identified as Taliban were sentenced to death for murdering a Frenchwoman who worked for the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees. They had gunned her down in Ghazni, a town sixty miles south of Kabul, in the middle of the afternoon. A few weeks ago, one of Louis Berger’s helicopters was attacked near Kandahar. The Australian pilot was killed, and an American engineer was seriously injured. Not long after that, the director of the Afghan Red Crescent office in Zabul province was shot by armed men on a motorcycle. Joseph Collins, a deputy assistant secretary in the U.S. Department of Defense, says that the attacks against aid workers and people employed by foreign contractors are part of a well-defined strategy. For the Taliban, “reconstruction is Enemy No. 1,” he explained. The attacks are not being carried out by simple criminals. “People sometimes refer to them as brigands, but they are Taliban, Al Qaeda, and Hezb-e Islami”—the fighters of the vicious Pashtun warlord Gulbuddin Hekmatyar. (Hekmatyar, who received more money from the U.S. and Pakistan than any other jihadi during the Soviet occupation in the nineteen-eighties, was in exile in Iran during the years that the Taliban controlled Afghanistan, but he formally allied himself with them after September 11, 2001. He is now in hiding.)
The road was built in the early nineteen-sixties, with money and equipment contributed by the United States, during a period in which the Americans and the Soviets were vying for influence in Afghanistan, and it was destroyed during the Soviet occupation. In the late nineties, the Taliban laid asphalt on the first twenty-seven miles south of Kabul. I travelled on the road several times when the Taliban were in power, and then in the aftermath of the war, and it was a hellish experience. It took sixteen hours to drive the three hundred miles between the two cities. The road was like a dry riverbed, undulating and full of boulders, with blown-up bridges and craters that gouged the underbellies of cars. The last time I was on the road during the Taliban regime was in the spring of 2001. As my travelling companion, Amir Shah, a colleague working for the Associated Press, and I drove out of Kabul, we saw what had become commonplace in Afghanistan then: at a checkpoint, two steel girders on either side of the road were draped in yards of brown tape ripped from music cassettes that had been confiscated from travellers. We pulled up to the checkpoint just minutes after the minister of vice and virtue, Nooruddin Turabi, got there. Turabi, the author of some of the most ludicrous of the Taliban’s edicts, like the one outlawing white socks on women, was sitting beneath a mulberry tree, out of sight, but the guards were still shaking. He had just slapped one of them hard across the face, as punishment for listening to music. The guards wore the unkempt beards demanded by the Taliban, but they were young and had been listening to a tape of their favorite singer, Naghma, a famous Pashtun songstress from Kandahar. They hadn’t heard Turabi’s pickup truck pull in. “Go—go quickly. Just go,” they told us.
The checkpoint outside Kabul today is rather different from what it was three years ago. When Amir Shah and I set off for Kandahar recently, we were stopped by guards from the interior ministry commanded by a clean-shaven officer in a green wool uniform who watched as his men searched vehicles with music screaming from the dashboards. And there was a female guard, a soft-spoken young woman named Shafiqa, who wore a black shawl that sparkled with silver sequins. The shawl covered her face, so that only her eyes and a single strand of dark-red hair were visible. Shafiqa’s job is to search female travellers. Mostly, she looks for drugs.
A marble slab on a gray stone pedestal stands at Kilometre 43 on the road to Kandahar, where the section of new highway completed by the Louis Berger Group was inaugurated in mid-December. The monument bears an inscription in Farsi, Pashto, and English: “In memory of those who gave their lives in the reconstruction of this road unifying all the people of Afghanistan.” The new highway is the first big reconstruction project to be completed in Afghanistan since the Taliban were defeated. Most projects have been small—a school here, a well there, a clinic somewhere else. The road was not expected to be finished until 2005, but last spring President Bush decided that it had to be open by the end of 2003. The work was accelerated, Vikram Parekh, an analyst for the International Crisis Group, said to me, because the Bush Administration badly needs “a success story” this year. “Iraq is not a model of stability,” Parekh noted. “And there are two political deadlines looming: the Afghan Presidential elections”—which will probably take place in the fall—“and the Presidential elections in the United States.” When additional layers of asphalt are put down and further work is done, sometime later this year, the highway will have cost the United States two hundred and seventy million dollars. The American contribution was originally budgeted at eighty million, which included funds for the road from Kandahar to Herat—another three hundred and fifty miles. “It just goes to show what you can do when money is no object,” an American official in Kabul said.
Almost no work had been done on the road when Bush set out the new timetable, and virtually no equipment was in place. Before construction could begin, the Indian and Turkish firms subcontracted by Louis Berger had to airlift in parts for their asphalt plants. More than a thousand mines and other ordnance, mostly left over from the war with the Soviets in the nineteen-eighties, were removed from the area.
The terrain along the road is starkly beautiful. There are no power lines, just sunbaked mud houses that disappear behind swirls of dust whipped up by the wind. Irrigation ditches feed water to a land seared by five years of drought, and farmers squat on their haunches and use handheld scythes to cut the dry brush that they burn for fuel. Occasionally, you come across a band of nomads who have set up tents. Their sheep and goats nibble lazily on the brush, while women stoke cooking fires. The women wear heavy dresses embroidered in bright colors and decorated with small pins and tin buttons—anything, it seems, that might make a soft jangling noise as they walk.
At Kilometre 109, which is marked by a tiny piece of cardboard attached to a stick, we stopped to talk to Wazeer Muhammad Mamel, a man in a cream-colored shalwar kameez. He was on a bicycle, and a few of his friends were walking along beside him. Mamel complained that the road was too narrow and that people were being killed by speeding drivers who had probably never seen a paved road before, didn’t have a license, and most certainly had never taken a driving lesson. He said that a hundred and twenty people were killed in traffic accidents the first week the road was open. This figure seemed somewhat high, but as we talked cars sped past us, most of them going more than seventy miles an hour.
Mamel pointed a little farther on. “Look over there,” he said. “It’s a bus, although you can’t tell.”
What must have been a small van was sitting upright on the side of the road. Red and green tassels fluttered in the wind from its mangled roof. The windshield lay in a thousand tiny shards on the crumpled dashboard. The guts of the car spilled out—wires were twisted around one another, coils drooped down—and the engine, which had been smashed inward, was pressed against the crippled frame. Seats were shoved to the rear, and one was turned violently on its side. They were covered with bloodstains.
The van had collided with a truck and two people had died, we were told by a man in a black leather coat who said that his name was Agha Gul and that his cousin had been the driver. The cousin was badly injured. It was the truck driver’s fault, Agha Gul said, although his cousin had been driving too fast. The cousin wasn’t much of a driver, and when he saw the truck turning left he panicked and hit the gas pedal instead of the brakes. In keeping with Afghan tradition, the truck driver paid the victims’ families the equivalent of two thousand dollars. “We forgave him the deaths when he paid the money,” Agha Gul said.
We got back in our car and continued on—driving perhaps a little more slowly than we had before—and stopped at Abdul Ghaffar’s Nawid Restaurant and Hotel, a dingy two-story building set away from the road at the edge of Ghazni. Small shops on the first floor were packed with biscuits, candies, cans of Coke, shampoo. Business had fallen off since the road opened, Abdul Ghaffar said. People travelled at night now, which they hadn’t done before, and buses from Kandahar, which used to take two days to get to Kabul, no longer stopped. Ghaffar didn’t mind. “The road is good for Afghanistan,” he said. Prices of supplies hauled into Ghazni had gone down twenty per cent, because trucks made the trip from Kabul in a third of the time, with far fewer breakdowns. Ghaffar said that there were Taliban in the vicinity, but that they rarely came into town. He wasn’t worried enough to hide his television set, which he had retrieved from where he stashed it when the Taliban took over the area in the mid-nineties.
Perhaps a hundred thousand people live in Ghazni, most of them ethnic Pashtuns and Hazaras, who are mainly Shiite Muslims. It is a deeply conservative place. Women are rarely seen in the bazaar, a sprawling and congested area where horse-drawn carts rattle down the street, car horns blare, and shops are small and packed to the rafters. The governor of Ghazni, Azadullah, is a follower of Abdul Rasul Sayyaf, an extreme fundamentalist warlord who is now a power broker in Kabul. During the war with the Soviets, Sayyaf’s mujahideen included more “Afghan Arabs”—foreign fighters—than any other mujahideen group. In the early nineties, after the mujahideen took Kabul, Sayyaf controlled the Afghan Ministry of Interior. During this period, fighting among the warlords who made up the government in Kabul led to the destruction of the city and the deaths of fifty thousand of its citizens. Many of the same warlords are again in power, and Karzai has been unable to do much about this. They are in large part responsible for the instability of the country, and the subsequent resurgence of the Taliban.
We were invited to stay in Azadullah’s guesthouse, where a young boy pumped chunks of wood into a dirty black tin stove. Smoke seeped from cracks in a narrow pipe that twisted out of the room through an opening in the wall. The military commander of Ghazni, Ali Akbar Kasimi, a diminutive man with a wispy beard, sat with us, cracking his knuckles and talking about Taliban activity in the area. They disseminated warnings through shabnamah, night letters, he said, a tactic honed during the Soviet occupation, when mujahideen would scurry down from mountain hideouts with handwritten notes urging young men to fight against the infidel invaders.
Occasionally, the night letters are signed by Mullah Omar now. Their basic theme is “Fight against the foreign soldiers, don’t support the government or work for it, don’t send your girls to school.” The penalty for ignoring the warnings is usually death. A batch of shabnamah were found in Kandahar recently. One of them showed a U.S. soldier searching the pockets of a fifteen-year-old girl. It carried a harsh admonishment: “This picture shows the cruelty of the U.S. forces and their behavior against humanity. Where are those brave Afghans, those who used to sacrifice themselves to save the honor of their sisters? Where are those brave Afghans who used to pull out the eyes of those who had an evil eye on Afghanistan? Why are the imprints of the swords of the brave Afghans not seen on the chests of the Americans? Wake up, Afghans. Otherwise you will lose your honor.”
A building on the southern edge of town that housed a madrassa under the Taliban was now, we were told, the headquarters of an American military unit, and the next morning we left the new paved road and followed a dirt track toward an American flag that was flying over a low-lying cement structure. An armored personnel carrier was parked in front, and, as we approached, a soldier crouched behind the machine gun mounted on top of it. He relaxed a bit when I got out of the car and waved and called out in English, but he didn’t put his rifle down or move away from the machine gun.
The soldier was a member of one of the Provincial Reconstruction Teams that operate outside Kabul. The P.R.T.s, which have been in Afghanistan for a little more than a year, are the central element in the new United States pacification strategy for the south and the east. The United States has ten teams, some of them in development and several more in the planning stage. New Zealand runs one in Bamiyan province; Britain has one in Mazar-i-Sharif; and the Germans recently took over in the northern province of Kunduz. There are more than twelve thousand American soldiers in Afghanistan, most of whom are hunting down Taliban and Al Qaeda fighters. The soldiers in the P.R.T.s, which have between sixty and a hundred members each, are assigned to work peacefully alongside civilians from agencies like usaid, trying to persuade the locals to coöperate. This is especially difficult in southern Afghanistan, among the Pashtun population, which has received little assistance from the Americans or from the new Afghan central government, even though Karzai and several other ministers are Pashtuns. The Americans won the war as the allies of northerners—Uzbeks, Tajiks, and Hazaras—and the northerners were influential in establishing American policy, which marginalized the Pashtuns. Most of the military operations against Taliban and Al Qaeda fighters have been carried out on Pashtun land, often by militias loyal to northern warlords. Milton Bearden, who was the C.I.A. chief in Pakistan in the late eighties—when Pakistan was the staging area for the anti-Communist mujahideen bankrolled by the United States—says that one definition of the current Taliban is “a lot of pissed-off Pashtuns.”
The pacification and rebuilding process calls for constructing more than a thousand miles of roads, large hydroelectric dams, and civil-administration buildings, like courthouses. Security is to be improved by building new police stations and training village policemen. The Defense Department believes that the sight of U.S. soldiers rumbling through the region in Humvees and armored personnel carriers and fixing up Afghanistan’s infrastructure will encourage people who want to resist the Taliban and are not sure that they will be protected if they do so.
We were invited into the Ghazni P.R.T. headquarters and sat down at a long table with three “civil affairs officers,” Lieutenant Colonel Mark Schnur, Captain Dan Verich, and Staff Sergeant Laura Putze. They were Army reservists. Captain Verich said that villagers knew right away that they weren’t combat soldiers, even though they wore khaki camouflage uniforms and were accompanied by heavy weapons. Sergeant Putze explained that their headgear made the difference. They wore baseball caps rather than helmets. Lieutenant Colonel Schnur, who has a patient, thoughtful demeanor, said that P.R.T. soldiers don’t come into a village yelling and kicking in doors; they offer a friendly wave and try to find the local elder. “We want them to know that we are here to get rid of the bad guys and reward the good guys,” Schnur said. But in southern and eastern Afghanistan war often intrudes on rebuilding efforts. There had been a particularly violent intrusion in Ghazni province recently, in the village of Peetai, when rockets from U.S. fighter jets killed nine children and a young man who had returned home from Iran just three weeks earlier to get engaged. The rockets were meant for someone who was described first as a terrorist and then as a murderer of two road workers. In any case, he wasn’t in Peetai at the time of the rocket attack.
Captain Verich said that the P.R.T. had been to Peetai the day before we arrived in Ghazni, and that the villagers were not openly angry. The soldiers had offered their condolences and help. “We told them we would build a well, not as compensation or anything but because they needed one,” Captain Verich said.
Peetai is a village of mud-brown houses surrounded by parched fields. We could see the graveyard as we drove up. Thin sticks draped in brightly colored pieces of cloth, a traditional grave marker that often indicates the burial place of a martyr, had been placed in the rocky ground around ten mounds of earth. In front of the graves, several small children and a few young women had formed a semicircle around a woman draped in a large black shawl. The youngest children pushed and shoved one another. Men stood nearby, protectively. The woman in the black shawl didn’t move as we approached. The shawl covered her face, except for one eye, which was swollen and red. Her name, one of the other women said, was Aysha Bibi, and she was the mother of the young man who was killed after he came home to find a bride. He had been fetching water when the jets attacked.
Aysha Bibi wasn’t crying anymore, and once she began speaking she talked in a steady stream, hardly stopping to take a breath. “We have nothing,” she said. “No food, no money, no water. We are eating dust. What were they looking for? What have we done?” Aysha Bibi is a widow. Her husband was a mujahideen who was killed by the Soviets in the nineteen-eighties. She has two other sons, both in Iran, and three daughters, who live with their husbands in the village.
One of the village elders, a frail man with a white beard, described the jets flying in low over the fields where the children were playing. He, too, was angry at the Americans. “We want them to leave—we don’t want their help,” he said when I mentioned to him that the reconstruction team intended to build a well. The only well the villagers had now wasn’t working. The pump handle had been missing for as long as anyone could remember. The elder didn’t care. “Let them keep their well,” he said.
The house of Mullah Wazeer, the man the fighter jets had been sent to kill, overlooks the field where the children died. There’s a memorial there now: three tiny piles of rocks just outside Wazeer’s house and, a few hundred feet away, six more piles. A tall, balding man was standing there, his head bent. His name was Zarwar Khan, and his only two sons had been killed in the attack. Hamidullah Khan, his brother and the father of another of the dead children, did most of the talking, slipping between anger and sadness. He said that two women had miscarried after the attack, and he raged about the soldiers who had taken control of the village and had refused to allow the children’s parents to claim the bodies for twelve hours. Devout Muslims wash their dead and shroud them in a white cloth and bury them before sunset on the day they die.
Hamidullah Khan didn’t let us get away easily. He was contemptuous of the soldiers who had visited the village the previous day. “They brought the children some balls and things, and clothes,” he said. “What is that supposed to do for us?” His eight-year-old son stood close by him, listening. The boy seemed small for his age, but that might have been because of the oversized coat he wore, a bright pink-and-blue winter coat that came almost to his knees. His hands sank into the pockets. It had been given to him by the American soldiers. He also wore an adult’s baseball cap, pulled tight at the back to fit his tiny head. The boy had to tilt his head slightly to see beyond the brim, which was emblazoned with a small American flag and the words “Columbus Ohio.”
Zabul province, which is just south of Ghazni, is one of the most dangerous places in Afghanistan. Perhaps eight of its eleven districts are controlled by the Taliban, and the others are only nominally managed by the government. We left Ghazni for Qalat, the capital of Zabul province, early in the morning, and Amir Shah began speeding right away. By the time we got close to Shah Joy, where Mullah Muhammad Khaksar, the Taliban defector, had been attacked a few weeks earlier, the car was rattling. But we passed Shah Joy without incident, and soon could see the ancient mud fort that sits on a hill above Qalat, an old market town with rocky, unpaved streets. In the center of town, the big green steel gates of the governor’s office were protected by a mesh of security barriers. The guards let us through, and we were ushered into the governor’s office, which smelled of must. The governor, Haji Muhammad Hashim, a short man with a thick black beard, was flanked by four hulking military commanders wearing turbans with long tails. Hashim wore a karakul cap, like the one worn by Hamid Karzai, a portrait of whom hung over Hashim’s desk. Hashim explained that they are related, and that he had been with Karzai in the mountains of Uruzgan province early in the war against the Taliban. They had moved from one safe house to another, fighting alongside U.S. Special Forces.
The four military commanders had come to collect the wages of their soldiers and policemen. There was no safe in the room, and Hashim didn’t have a checkbook, but he pulled a packet of new thousand-afghani notes from an inside pocket of his leather jacket and divided them among the commanders, who counted the money and spoke to him for several minutes. Hashim turned to us and laughed. “It’s always a negotiation,” he said. “This one complains, ‘What about our cars? We need repairs.’ What can I say? I don’t have anything more to give them.” He said that—his relationship with Karzai notwithstanding—he wasn’t getting enough money from the central government.
Hashim offered us accommodations in his guesthouse, and we were shown to a box-like cement room furnished with a broken-down cabinet and a steel bed that held a cushion crawling with tiny bugs. Two more cushions had been tossed on the floor, next to a potbellied woodstove. The washroom, which the governor’s secretary explained was used only by special guests, was black with dirt, and the toilet, which had no seat, didn’t flush. There were what seemed to be footprints on the rim of the toilet bowl.
The deputy governor, Muhammad Omar Khan, brought his brother-in-law, a lanky young man named Humdullah, in to meet us. Humdullah sat down on the floor slowly, easing himself against the sooty wall. He didn’t speak at first, and Omar Khan explained that he had been beaten up recently by Taliban. Ten of them had stormed into his house with guns, their faces covered. Humdullah held a shawl over his mouth and nose to demonstrate to us what they looked like. Omar Khan said that the beating had gone on for several hours, and Humdullah pointed to his legs and his side. They had broken several of his ribs, and his legs were bruised and sore. The Taliban wanted to know what the government was planning. They wanted his phones, his guns. When it was over, they blindfolded his younger brother and shoved him into the back of a pickup truck and drove him to another relative’s home, where they stole a motorcycle. Omar Khan said that this was all because he was the deputy governor, working for Karzai.
Omar Khan decided that the room in the governor’s guesthouse was inadequate, and he took us to the Afghan Development Association office, on the outskirts of Qalat, across the street from the police station. We would be safe there, he said. The Afghan Development Association is a charity funded by the government and the European Union, and is one of only two international aid organizations still operating in Zabul province. The director, Abdul Ghani Tokhi, a quiet man with a long white beard, said that he and his colleagues built irrigation ditches and encouraged local councils to propose other construction projects. Omar Khan and Tokhi concurred about the increasing power of the Taliban. Omar Khan said when the Taliban collapsed, in December, 2001, more than two thousand men came to Qalat ready to work with the government and to fight with Karzai. They stayed for two months or so, but since there was no money for salaries, food, or shoes they returned to their villages. Now, Omar Khan said, most of them are with the Taliban.
The new Afghan National Army has the same problem. Yaqub Khan, the deputy commander of the Army in Qalat, said that only two of the forty-two men from Zabul he sent to be trained as professional soldiers are still with him. The other forty have joined the Taliban. “They’re illiterate,” he said. “They don’t know. The Taliban are strong in their areas, and they join them.”
The final thirty-one miles of the highway to Kandahar was built by the Japanese government. It’s the worst stretch, with a thin layer of asphalt and in some places no new pavement at all. As you approach the city, there is what looks like a hopeful sign for Afghanistan’s future. Steel beams peek through the cement girders of a nascent industrial park. A textile mill is being built next door to a new row of shops. But there are also monuments to the past: the rubble of Mullah Omar’s elaborate compound, for instance, and the cavernous Eid Gah mosque and madrassa, supposedly commissioned by Osama bin Laden. Deadly bombings are another reminder that Kandahar was the Taliban’s capital, and that they haven’t gone away. In January, thirteen people were killed, many of them children playing in a soccer field, when a bomb exploded on the eastern edge of the city. Kandahar province, like Zabul, borders Pakistan, which has allegedly been letting Taliban fugitives come and go with impunity.
The province, which is one of the largest poppy-growing areas in Afghanistan, has a new governor, Yusuf Pashtun, who four months ago replaced the corrupt warlord Gul Agha Sherzai. The warlords who have run Afghanistan since the fall of the Taliban finance their private armies and prisons through extortion, theft, and the flourishing drug trade. (Poppy production is more widespread than ever before in Afghanistan, which is, once again, the world’s leading producer of opium. The opium trade brought in $2.3 billion last year. The warlords, who are government ministers, military commanders, and regional administrators, receive the bulk of the profits.)
After Gul Agha Sherzai was removed from his job as governor of Kandahar, he was made the urban-affairs minister in Kabul. The new governor, Yusuf Pashtun, wants to make changes, to give people something they will want to protect. “They are apathetic,” he says. “They have nothing to lose. No roads, no wells. Give them something to build, something to which they can be attached.” For this, of course, one needs security. “It’s not so much that the Taliban are in control,” Pashtun said to me. “It’s that we haven’t established an alternative.” The government can’t get aid to the outlying areas because they are insecure, and they are insecure because no aid is getting to them.
“The situation is reminiscent of what was witnessed after the establishment of the mujahideen government in 1992,” Lakhdar Brahimi said in December, shortly before the completion of a two-year stint as the United Nations special envoy to Afghanistan. “The spectacular rise of the Taliban then was a direct result of the hard, unjust, and chaotic rule of the mujahideen rather than due to any enthusiasm for Taliban ideology.”
This, of course, is what the Americans have in mind as they deploy the new Provincial Reconstruction Teams. Joseph Collins, at the Defense Department in Washington, explained to me that one couldn’t really think about “conflict” and “postconflict” anymore. Instead, you have “War A, followed by War B,” which is the stage we are in now. “The complicating factor with War B is carrying out military operations and doing reconstruction work at the same time,” Collins said. “But the mix is inevitable.” Perhaps. Yet, even if the P.R.T.s manage to build dams and new roads, will people be able to use them freely? “Reconstruction projects may generate some good will, but they won’t guarantee security,” Vikram Parekh, the analyst at the International Crisis Group, said. “What’s required is police training, judicial and civil-service reform, and the disarming of the militias.” It’s hard to imagine that this sort of rehabilitation will occur in Afghanistan as long as the fighting with the Taliban and Al Qaeda goes on, and unless enough money is available to underwrite more success stories—even relative ones, like the new road between Kabul and Kandahar. What’s really needed is a strong national government that works and that can rein in the warlords and government ministers who threaten to turn Afghanistan into a narco state that rivals Colombia.
0 Comments:
| "Join this group" مجموعة العروبيين : ملتقى العروبيين للحوار البناء من أجل مستقبل عربي افضل ليشرق الخير و تسمو الحرية | ||

|
Subscribe to Arab Nationalist | |
| Browse Archives at groups-beta.google.com | ||

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License.

Anti War - Anti Racism
Let the downFall of Sharon be end to Zionism

By the Late, great political cartoonist Mahmoud Kahil




































